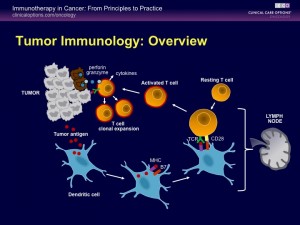
DENDRITIC CELLS are part of our immune system. They play a key role in fighting cancers by first recognizing the unique features of the cancer and then by instructing the T cells and killer cells to destroy them. This is called Cancer Immunotherapy. Our program combines Gene Therapy using Gendicine with Cancer Immunotherapy for the best results in patients with advanced cancers.
Learn about the genes that predispose a person to cancer, and the tumor suppressor genes that help protect us from cancer. Originally published in Rappler.com http://www.rappler.com/science-nature/ideas/49177-good-genes-bad-genes
MANILA, Philippines – Each person has around 24,000 genes, which can be compared to computer programs that determine our personal traits: what the color of our hair and skin are, what our height is,how intelligent we are, and what diseases we are susceptible to, such as heart disease and cancer.
The genes are inherited from our parents. They are the starting points of our life. However, not all genes will be “expressed” unless the condition is right.
For example, a person prone to heart disease will not necessarily develop heart disease unless his eating and lifestyle habits allowed the disease to manifest itself.
Thus, to a certain extent, genes are not destiny. We are able to modify what becomes of us even though we are born with the genes.
Genes and cancer
Among the genes many people inherited are oncogenes, which are genes that predispose a person to cancer.
There are now many known oncogenes, such as those for cancers of the breast and colon. On the other hand, we also have tumor suppressor genes that help protect us from cancer.
Many of these genes can now be detected by a genetic test. Many of us have heard the story of Angelina Jolie, who opted to have both her breasts removed when she learned that she has the BRCA gene mutation, which predisposed her to breast cancer.
The detection of these genes allows us to do something that can decrease the risk for cancer, such as changes in diet, physical activity, intake of medicines, even surgical intervention.
For example, the drug tamoxifen can also help reduce the risk for breast cancer among those with the BRCA gene mutation. Meanwhile, a diet low in animal fats plus avoidance of alcohol and smoking will go a long way to minimize colon cancer risk.
One of the most important tumor suppressor genes is p53, which is found in the short arm of chromosome 17. It plays an important role in how fast cells divide. Defective p53 allows abnormal cells to multiply very fast, resulting in cancer.
The presence of damage to the genes, which can be due to radiation, chemical toxins or environmental carcinogens from cigarette smoking, will trigger an increase of p53 proteins, which will act to stop cell multiplication, thus preventing replication of damaged genes.
At the same time, p53 may help the formation of proteins involved in the repair of genes.
If both these steps failed, the p53 protein will then initiate a series of steps that program the cell itself to die, called apoptosis.
By killing the cell that is becoming cancerous, the p53 protein in effect prevented the growth and spread of cancers.
It’s known that more than 50% of cancers have defective p53. And it is also known that inserting a normal p53 into cancer cells, which is easily done in the laboratory, can induce them to undergo apoptosis.
Trojan horse and other innovations
However, for decades, the problem was how to put normal p53 genes into the cancer cells of a living person.
An ingenious solution was to insert a normal human p53 gene into the common colds virus – an adenovirus. By genetic engineering, the ability of the virus to multiply was destroyed at the same time.
This recombinant human adenovirus-p53 organism, since they are essentially common colds viruses, are highly infectious and can easily enter our cells.
The virus is thus like a Trojan horse, with the p53 gene as the warrior inside.
When injected into the vicinity of a cancerous mass, the viral particles enter the individual cancer cells and do their job of inducing mass cell suicide. There is no damage when they enter normal cells.
As science continues to discover new genes for specific diseases, we will be able to diagnose, prevent, and treat them better.
At the same time, diet, exercise, and a positive outlook can modify how the genes are expressed and thus are still very important for health. – Rappler.com
Dr. David Dy is a surgical oncologist at the St. Luke’s Medical Center (Global City). He got his medical degree at the UP College of Medicine, cum laude, and a Master of Surgery at the University of New South Wales in Australia. He is a fellow of the American College of Surgeons and the Society of Surgical Oncology. His interest is to find new ways to help improve the treatment of cancer.
Here is the audio recording of the interview of Dr. Amy Goleta-Dy on the Healthcare Plus radio show.
Gene Therapy Interview with Dr. Amy Goleta-Dy
What do Tom Hanks, Julia Roberts and Gwyneth Paltrow, Michael Douglas, Matt Damon and Robert Pattinson have in common? How about Taylor Swift, Alicia Keys, and Tim McGraw? Aside from being celebrities, they also helped create awareness and raise funds for cancer research and treatment. They and other celebrities and athletes were involved in the 3rd Stand Up to Cancer telethon on September 14, 2012. And many of them have personal experiences with cancer or have close relatives who had it.
Cancer is a serious disease. In the U.S., 1,600 Americans die of cancer every single day. One in two men and one in three women will be diagnosed with cancer in their lifetime. And according to Roberts, “Cancer kills a child every 4 hours”.
The statistics in the Philippines are bad also. In fact, it is rare for anybody not to have a family member, a friend or a colleague who wasn’t treated for or died from cancer.
Nevertheless, due to the continuing support of many individuals and corporations for Stand Up to Cancer and other organizations, newer innovative treatment modalities to improve the quality of life and survival of cancer patients became reality.
Chemotherapy works by blocking the replication of fast-dividing cells such as those found in cancers. Scientists have observed that cancer cells are so easy to kill in the laboratory using chemotherapy medicines, and yet when chemotherapy medicines are actually injected into patients with cancer, the effect is not as impressive. In fact, some cancers continue to grow and spread.
One possible reason was recently discovered by researchers in the United States. They found that chemotherapy can damage normal or healthy cells as well, which then secrete more of a protein called WNT16B, which enhances cancer cell survival. This unexpected finding was reported by study co-author Peter Nelson of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle. As he explained, the protein was taken up by cancer cells, which made them grow, invade, and more importantly, resist subsequent therapy. This is also the reason for the observation that cancers often respond well initially to chemotherapy, but will grow rapidly later on and become resistant to further chemotherapy. In fact, many oncologists have also observed that cancer cell proliferation accelerates in-between chemotherapy.
Their findings may result in newer and better treatment. One option is to develop antibodies to block WNT16B. Another way may be to use a smaller dose or less toxic chemotherapy so that normal cells don’t get damaged. When combined with gene therapy like Gendicine, which lowers the resistance of cancer cells to chemotherapy, a lower and less toxic chemotherapy may be the solution.